Managing a server comes with the responsibility of ensuring its security. With numerous threats targeting servers in various ways, it's crucial to follow best practices to safeguard your Windows server. Here are some essential tips to help you enhance your server's security:
1. Disable the Administrator Account
One of the most common ways attackers try to breach servers is through default system accounts. On Windows servers, the main target is the Administrator account. To reduce the risk of brute-force attacks, it's best to disable this account and create an alternative user with full administrative privileges. After creating the new user, go to Computer Management → Local Users and Groups
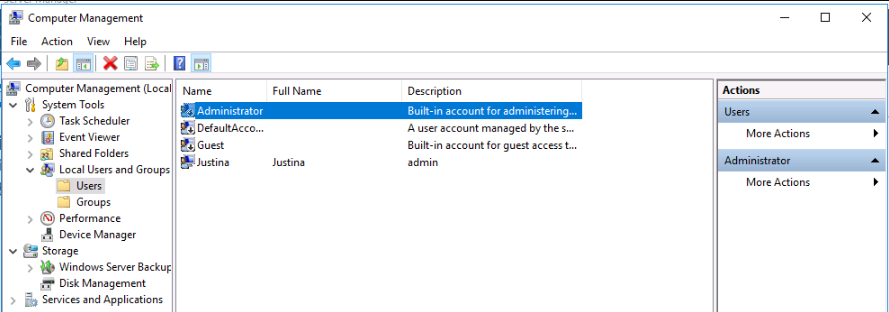
Right-click the Administrator user, select Properties, and check the box for Account is disabled.
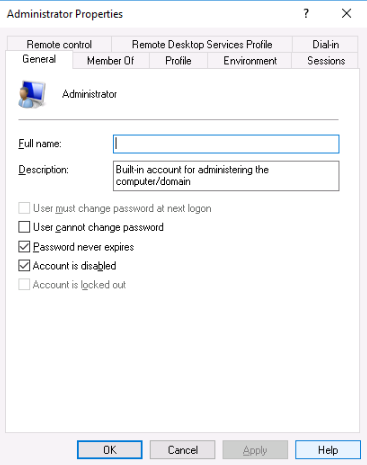
2. Set a Strong Password for Your Administrator Account
Hackers often utilize large databases containing potential passwords and their hash values to crack passwords. Therefore, it's vital to create strong, unique passwords that aren't found in dictionaries and to update them regularly. Use a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. For example, instead of using "OrangeCat," try "0r4ngeC4t." The longer and more complex the password, the harder it is to crack.
3. Change the Default RDP Port
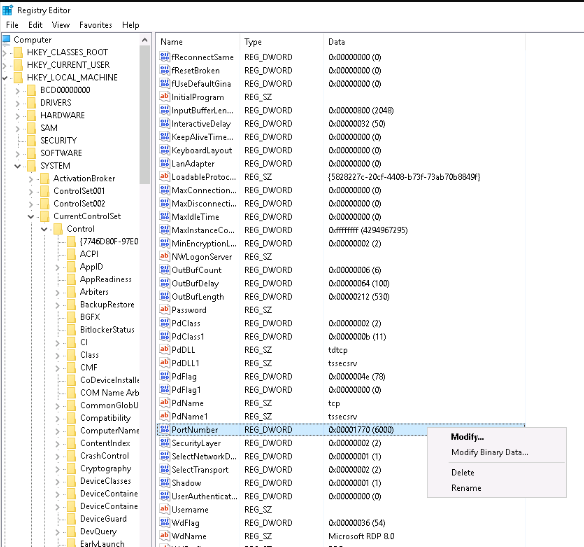
Just like changing the default SSH port on Linux servers, it’s a good idea to change the standard Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) port on Windows servers from 3389 to something else. To do this, open the Registry Editor by pressing Win + R and typing regedit. Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Control / Terminal Server / WinStations / RDP-Tcp
Right-click on PortNumber, select Modify,
In the newly opened window, you will see Value data. The value will be unclear, but you will see the port by selecting Decimal Base on the right. Put your port value there
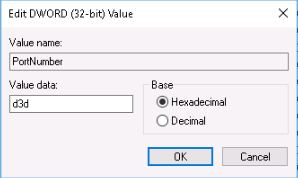
Change the port value. Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to change the RDP port with this command:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber" -Value 3390
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'RDPPORTLatest' -Profile 'Public' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 3390
If your firewall is enabled, ensure the new port is allowed.
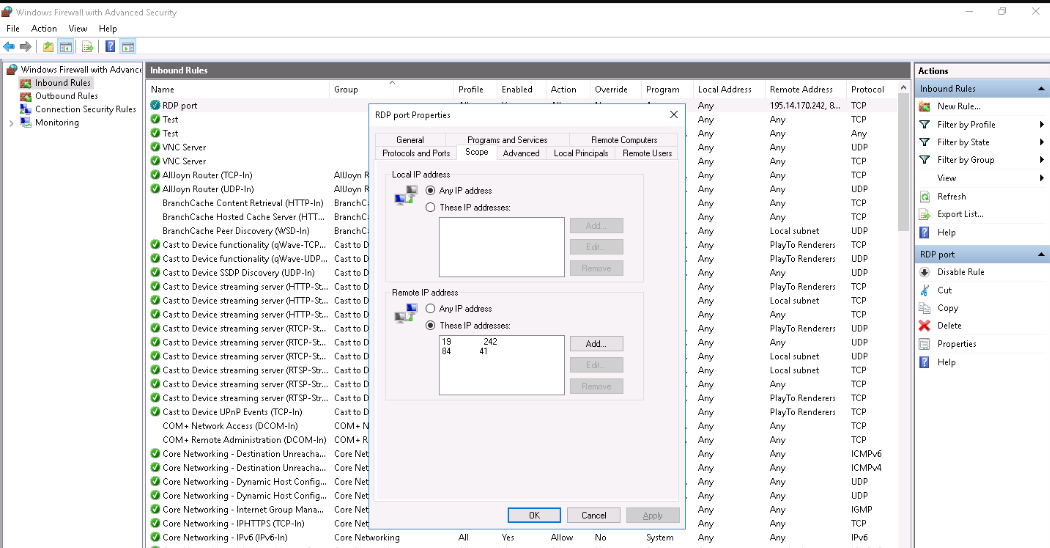
4. Restrict RDP Access to Specific IP Addresses
To enhance security, limit RDP access to specific IP addresses using your firewall. Locate your RDP firewall rule, right-click, select Properties, and navigate to Scope. In the Remote IP address section, add the IP addresses that are allowed to access the server via RDP.
5. Keep the Windows Firewall Enabled
The firewall is your server's first line of defense. Although it may consume some resources or block certain services, it's essential for filtering traffic and protecting the server from malicious activity. Keep the firewall enabled and configure it according to your needs.
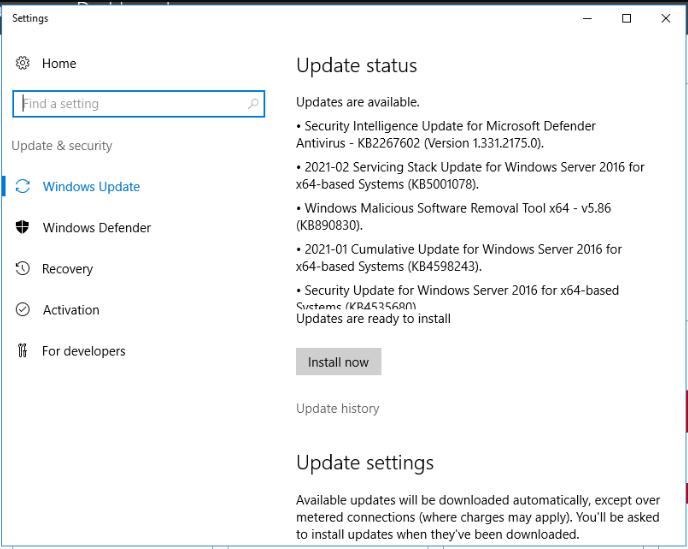
6. Perform Regular Updates
Updates are crucial for optimizing server performance and addressing security vulnerabilities. Regularly update both your operating system and installed software to protect your server from exploits. To install updates, go to Settings → Update & Security → Windows Update.
If you run a WordPress website, make sure to update WordPress and its plugins regularly as well.
7. Use Third-Party Security Solutions
Consider using antivirus software to enhance server security. There are both free and paid solutions available, such as Avira, Panda, Sophos, and Kaspersky. However, ensure that any third-party software is reputable and won’t unnecessarily drain your server's resources.
Conclusion
Basic server security is no longer just recommended; it's becoming mandatory. With the increasing sophistication of threats, failing to secure your server could lead to severe consequences, such as data breaches or financial loss. Take the time to implement these security measures to protect your server and your business.